Author Archive
 Hidden Gem: W0C/SP-076 Unnamed SOTA Summit
Hidden Gem: W0C/SP-076 Unnamed SOTA Summit
Walt/W0CP had recommended this Summits On The Air (SOTA) summit (W0C/SP-076) to me a while ago. Somehow it had escaped my attention, probably because it’s an unnamed peak and not that well known. Joyce/K0JJW and I decided to give it a try today and it turned out great.
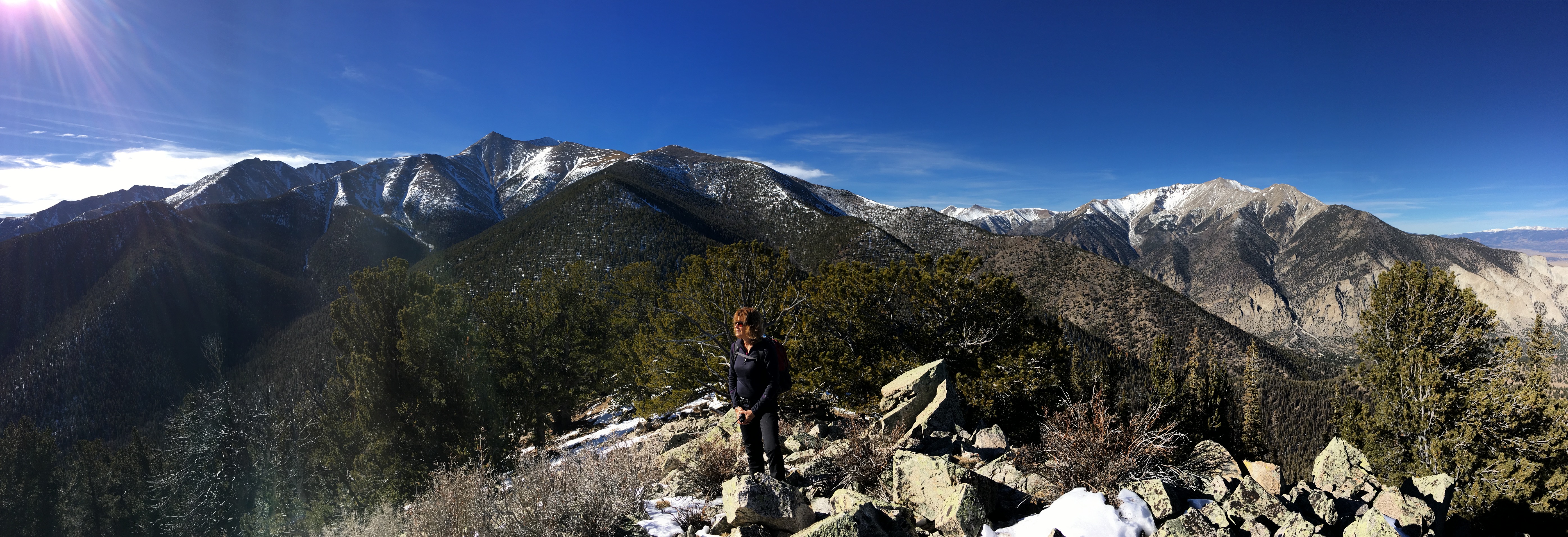

We followed Walt’s directions on the SOTA website, using the southern route. We were pleasantly surprised to find a pretty good trail most of the way to the summit. There were a few spots with downed timber, where people have diverted around the logs, but generally the trail was easy to follow. The trail is not shown on many maps, including the USFS San Isabel Forest map. Thus, I was expecting considerable bushwacking to get to the summit.
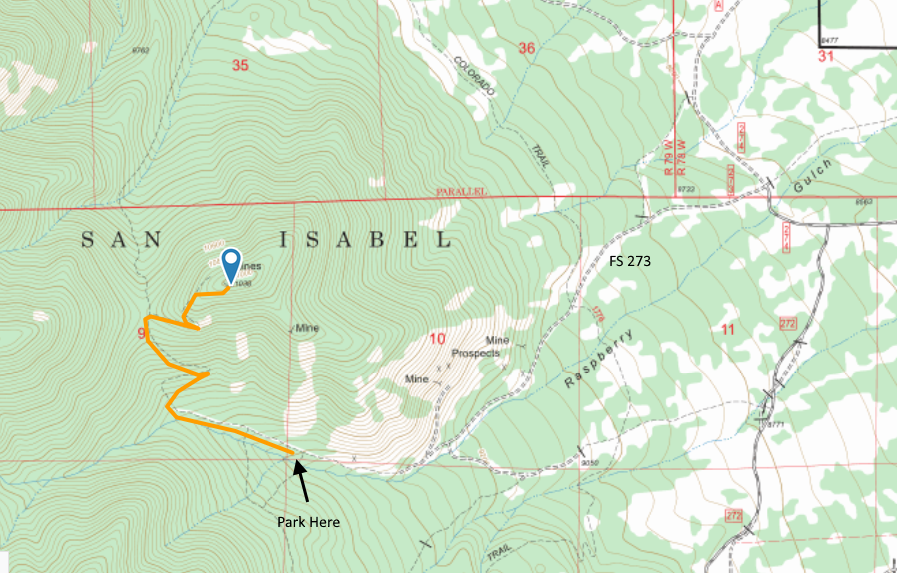
The route to the trailhead is via FS Road 273, easily accessible from Highway 285 south of Buena Vista and north of Salida. See the San Isabel National Forest map for orientation. The road is narrow in spots. Our Jeep Wrangler fit OK but a wider vehicle would get to deal with the brush on both sides of the road. The road is easy 4WD and should be passable with a high-clearance 2WD vehicle. The road had some snow on it (Nov 25, 2017) and with a few more snowstorms may not be passable.

The road continues a little further than indicated on our topo map but it is obvious when it ends. After that, the road turns into a nice trail (our route shown on the map above). The trail has a few broad switchbacks that made for easy hiking. When we got near the summit, the trail was covered by many small snow drifts, so we opted to go off trail and just head for the summit. So our last quarter mile or so is probably not optimal for summer hiking. There are several mines at or near the top of the mountain.
We had quite a variety of radios with us, for 2m, 1.25m, 70 cm and 23 cm, FM only. We started on the workhorse band (2m FM) with the 25W Tytera radio and a vertical half-wave antenna. It seems that someone (me) left the 3-element 2m yagi antenna at home. We quickly made contacts with KD0MRC, W0BV, KD0VHD, KE0DMT and KL7GLK on 2m and/or 70 cm. I used my Alinco 222 MHz handheld to work KD0MRC on 223.5 MHz, which is apparently the first 222 MHz SOTA contact in Colorado. (Yeah, not a popular band.)
For the most part, it was pleasant on the summit, about 40 degrees F, but it got cold whenever the wind picked up. Without the wind, it was great. With the wind, kind of cold.
This is a great hike and a great summit. Only a few people have activated it for SOTA, so I wanted to write it up for others to consider. We will definitely return to this one due to it’s excellent combination of easy accessibility, good trail and wonderful views.
73, Bob K0NR
The post Hidden Gem: W0C/SP-076 Unnamed SOTA Summit appeared first on The KØNR Radio Site.
 Is the Internet Destroying Amateur Radio?
Is the Internet Destroying Amateur Radio?
 How many times do you hear the comment “ham radio…do people still do that?” followed by the statement that “surely the internet has made ham radio obsolete.” For the most part, that misses the point about the use and attractiveness of amateur radio. And yes, that is a clickbait headline.
How many times do you hear the comment “ham radio…do people still do that?” followed by the statement that “surely the internet has made ham radio obsolete.” For the most part, that misses the point about the use and attractiveness of amateur radio. And yes, that is a clickbait headline.
I’ve written before that Amateur Radio Is Not for Talking and that the Universal Purpose of Ham Radio is to have fun messing around with radios. One significant statistic is that the number of FCC amateur radio licensees remain at an all time high. Eventually, the demographics will likely catch up with us and this number will start to decline, but it hasn’t happened yet.
The internet has become a tool that is used to complement amateur radio, often in ways that we may not have predicted. Although there are plenty of “keep the internet out of amateur radio” folks in the hobby, there are many more that have found clever ways to make use of the internet. I view emerging technologies and technological innovation as unstoppable forces that will impact us whether we try to ignore them or not. Using that lens, let’s examine the impact of the internet on amateur radio.
Here are a few broad categories of impact:
1. Communication Pipe
The internet is often used to provide an additional mechanism for transporting ham radio communications. Obvious examples are VoIP systems such as EchoLink and IRLP. Also included in this category are digital voice systems that use the internet to connect radios together: D-STAR, Yaesu System Fusion, Brandmeister Network, DMR-MARC Network. WinLink is a global email system using ham radio. The core transport technology is the Internet Protocol Suite (TCP/IP) which is not limited to the public internet. Some ham radio organizations are implementing IP links using microwave gear on the amateur radio bands so they are independent of the internet.
Another application in this category is remote operation of ham stations. That is, use an internet connection to control a ham station at another location. Sometimes people refer to this as the Long Microphone Cord Model (or maybe I just made that us). Hams do this with their own private stations but there are also shared stations established by radio clubs and commercial vendors (see Remote Ham Radio). With community restrictions on external antennas being very common, having a remote station available is very attractive.
This has turned out to be quite disruptive because so much of ham radio operating depends on your location, which is generally determined by the location of the transmitter. But now you can have a person sitting in downtown Denver operating a transmitter that is in Fiji. Kind of confuses things a bit. Regulatory issues also come into play: that transmitter in Fiji is going to fall under Fiji regulation which usually means needing an amateur radio license issued by the local government. The day is coming when a DXpedition to a remote island will consist of a helicopter delivery of a remote radio box (with satellite link and self-deploying HF antenna) that is operated by someone sitting at home using their smartphone.
2. Reporting and Coordination
Ham radio operators also use the internet for spotting and reporting purposes. Spotting has been around for a long time, which basically means letting other hams know that a particular station is on the air and can be worked from a particular location. Hams have done this without the internet but the internet certainly allows for more efficiency. Or at least a lot more spots. DX Maps is a good example of a spotting web site that supports lists and mapping of spots.
Radio hams also use the internet for coordinating radio contacts. One of the most extreme examples is the use of pingjockey for arranging meteor scatter communications. Typically, two hams will connect on pingjockey and agree to try a meteor contact on a specific frequency, with specific timing, etc. This technique is easy to abuse, either intentionally or via sloppy operating habits, because you can inadvertently share the radio contact information via the internet. However, properly used, pingjockey is a wonderful tool that promotes meteor scatter operating. ON4KST operates an amateur radio chat website that enables a wide variety of online communication and coordination between hams.
The Reverse Beacon Network (RBN) is a network of radio receivers listening to the amateur bands and reporting what stations they hear. These stations are often referred to as CW Skimmers because they skim the CW information from the received signals. RBN began with decoding CW but now also supports RTTY. There’s no fundamental reason it couldn’t be extended to other modes, even voice modes, with sufficient computing power.
PSK Reporter is a similar reporting system which accumulates signal reports from HF digital stations. As the name implies, it was first focused on PSK31 but has expanded to include other digital modes.
3. Logging and Confirmations
For decades, hams have been keeping their radio logs using a wide range of software that is available. This is a handy way of keeping track of radio contacts and tracking progress towards operating awards. More recently, online systems have been developed to allow radio contacts to be confirmed electronically. That is, instead of exchanging QSL cards as confirmation of a radio contact, both hams submit their log information to a central server that records the radio contact. The ARRL offers the Logbook of The World (LoTW) which supports these awards: DXCC, WAS, VUCC and CQ WPX. The eQSL web site was the first online QSL site, offering electronic QSL card delivery and its own set of operating awards. Club Log is another online electronic logging system. The popular qrz.com web site has added a logbook feature to its set of features.
Electronic confirmation of radio contacts is a huge improvement for ham radio. While many of us still enjoy getting a paper QSL card, collecting QSLs for awards is a royal pain. Mailing QSL cards is expensive, takes time and often involves long delays.
Impact on Amateur Radio
Here’s my analysis of the situation: Categories 2 and 3 mostly represent a net positive influence on amateur radio. These are straight up information age applications that provide useful and quick updates about radio propagation and radio contacts. Yes, there is some downside in that many hams become dependent on them instead of doing it the old fashioned way: turn the big knob on the radio and listen. Not a big deal given the benefits.
Category 1 is more of an issue for me. The major effect is that it enables worldwide communication a lot easier while using ham radio. This is what causes many hams to say That’s Not Real Ham Radio when the internet is used to do so much of the work. Focusing on the actual radio wave propagation, there is really no comparison between working DX on the 15m band and making the same QSO with a UHF DMR handheld piped through the internet. At this point, I try not to overthink the issue, dropping back to The Universal Purpose of Amateur Radio is to Have Fun Messing Around with Radios. So if chasing DX on 15m floats your boat, keep on doing it. If the DMR handheld provides enjoyment for you, I’m OK with that, too.
Perhaps more importantly, we can’t really stop the impact of new technology. Oh, I suppose the amateur radio community could petition the FCC to restrict Category 1 use of ham radio. There could be regulations that limit the use of the internet being interconnected with Part 97 radio operation. However, that would have an even bigger negative impact on the hobby by arbitrarily restricting innovation. Imagine if we had to tell technically-minded newbies in the hobby that “well, we have this rule that says you can’t actually use the biggest technology shift in the 21st century” while using ham radio. We do have some rules concerning awards and contests such as you can’t use a VoIP network to quality for DXCC. There will probably be more of that kind of restriction occurring as technology moves forward, which is fine by me.
What’s Next?
When it comes to technological change, its often difficult to predict the future. Some of it is easy: we’ll see higher bandwidths and more wireless coverage on the planet as 5G and other future technologies roll out. Figuring out how this affects ham radio is a bit more difficult. Right now, there are still remote locations that aren’t on the network but that will change. I expect even remote DXpeditions to eventually have excellent connectivity which could lead to instant check QSLs. (That’s kind of happening already but it could become more of a realtime event.) As systems become smarter (e.g., machine learning, artificial intelligence), distributed systems will become more automated. We can expect more automation of ham radio activity which will certainly be controversial. Did you really work that other station if the software in your home ham station did it while you were away at work?
To wrap up, I don’t think the internet is ruining amateur radio but it is certainly changing it. The key is to keep having fun and enjoying the hobby. If you aren’t having fun, you probably aren’t doing it right.
What do you think?
73, Bob K0NR
The post Is the Internet Destroying Amateur Radio? appeared first on The KØNR Radio Site.
 My Twitter Novel
My Twitter Novel
This happened the other day on Twitter.
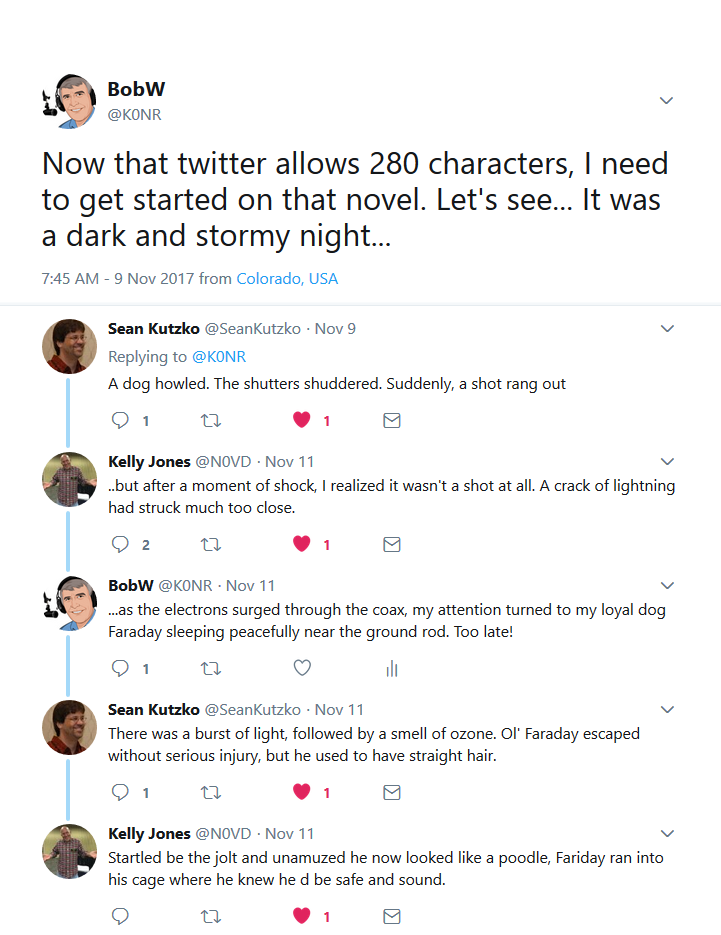 I thought it was funny. Thanks for the help, Sean and Kelly.
I thought it was funny. Thanks for the help, Sean and Kelly.
73, Bob K0NR
The post My Twitter Novel appeared first on The KØNR Radio Site.
 Colorado (W0C) SOTA Activators
Colorado (W0C) SOTA Activators
Here’s the SOTA activator scores for Colorado (W0C). I have to admit that I like checking this to see how everyone is doing. Some of it is friendly competition but mostly its enjoying the accomplishments of my fellow SOTA enthusiasts.
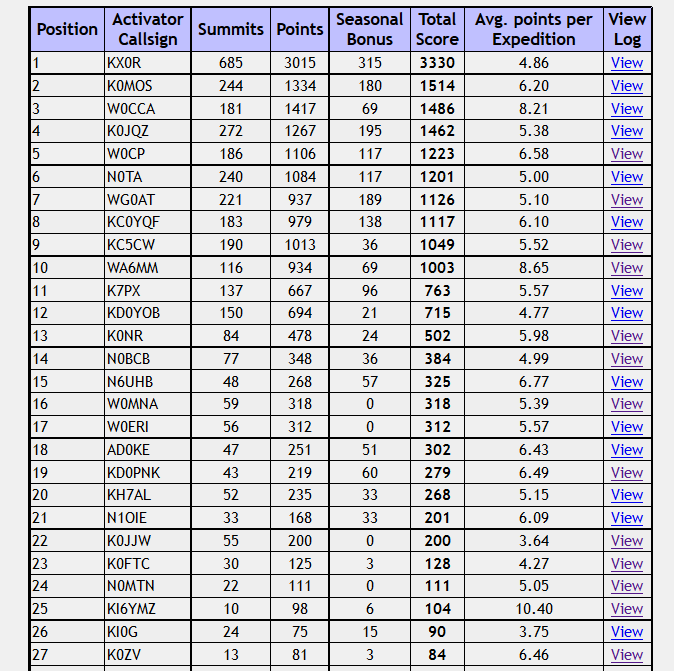 We’ve got 10 “Mountain Goats” in Colorado now, with 1000 or more points. Carey, KX0R just never stops activating. It seems like he is out there on a summit every day. My friend Brad WA6MM just made “Mountain Goat,” by activating only Colorado summits, never repeating any, with many difficult climbs. Note that his average points per expedition is 8.65, higher than any of the other MGs. (W0CCA comes close at 8.21) Congratulations, Brad!
We’ve got 10 “Mountain Goats” in Colorado now, with 1000 or more points. Carey, KX0R just never stops activating. It seems like he is out there on a summit every day. My friend Brad WA6MM just made “Mountain Goat,” by activating only Colorado summits, never repeating any, with many difficult climbs. Note that his average points per expedition is 8.65, higher than any of the other MGs. (W0CCA comes close at 8.21) Congratulations, Brad!
 It looks like K7PX and KD0YOB are next in line for Mountain Goat, while I am still a ways back. My hiking partner Joyce/K0JJW is coming on strong, having accumulated 200 points. I just cleared “half a Mountain Goat” at 500 points, so I requested a certificate for that accomplishment. At my current rate of progress, I am about 2 years away from Mountain Goat. I keep telling myself to be patient, keep at it and (most of all) enjoy the journey.
It looks like K7PX and KD0YOB are next in line for Mountain Goat, while I am still a ways back. My hiking partner Joyce/K0JJW is coming on strong, having accumulated 200 points. I just cleared “half a Mountain Goat” at 500 points, so I requested a certificate for that accomplishment. At my current rate of progress, I am about 2 years away from Mountain Goat. I keep telling myself to be patient, keep at it and (most of all) enjoy the journey.
73, Bob K0NR
The post Colorado (W0C) SOTA Activators appeared first on The KØNR Radio Site.
 More Power For VHF SOTA
More Power For VHF SOTA
 For years now, I’ve been doing Summits On The Air (SOTA) activations using VHF and higher frequencies. The GO TO band/mode for VHF SOTA is 2-meter FM because of its overall popularity. Just about everyone has a 2m FM radio (well, almost everyone). Still, if you are on a remote peak you may not find anyone within range to work. Because of this, it really helps to optimize the performance of your portable VHF station.
For years now, I’ve been doing Summits On The Air (SOTA) activations using VHF and higher frequencies. The GO TO band/mode for VHF SOTA is 2-meter FM because of its overall popularity. Just about everyone has a 2m FM radio (well, almost everyone). Still, if you are on a remote peak you may not find anyone within range to work. Because of this, it really helps to optimize the performance of your portable VHF station.
Antennas
I’ve already written that the first step is to upgrade the rubber duck antenna to something that actually radiates. My measurements indicate that a half-wave antenna performs 8 to 10 dB better than your typical rubber duck. That’s a big difference. I tend to favor the collapsible half-wave antennas because they are compact and don’t require any support. Another option is the J-pole or Slim Jim antennas, typically build out of twin lead or ladder line.
The next step up is to use a small yagi antenna, such as the 3-element Arrow antenna. Although Arrow does not specific the gain of this antenna, it has been measured at the Central States VHF Society conference as having ~6 dBd of gain. I’ve been on the lookout for a higher gain antenna but I have not found one that has significantly more gain while still being backpack portable.
Modulation
Frequency Modulation performs very badly when signals are weak. The well-known threshold effect means as the signal level decreases at the receiver it simply crashes into the noise. Linear modes such as CW and SSB work much better when signals are weak, which is why they are popular with the serious VHF crowd. I’ve used my Yaesu FT-817 to make SOTA contacts on both 2m and 70cm SSB and CW. My all time best distance on 2m during a SOTA activation was 229 miles, a QSO with N7KA from Capulin Mountain using CW. However, the problem with SSB/CW is that there are much fewer radio amateurs that operate that mode. I estimate that on a typical day, there are 10 to 100 times more hams on 2m FM than are on 2m SSB/CW.
More Power on FM
I’ve noticed that I sometimes hear stations on 2m FM but they cannot hear me. Further investigation revealed that they were typically running more power than me. I had my little HT putting out 5W and they were running a 50W mobile. That got me thinking about whether I could increase my power while still having a backpack-compatible station. SOTA operation is typically QRP, around 5 or 10 W of power. However, SOTA does not specifically state a required power level…it’s really driven by the need to operate backpack portable. Hence, there are very few 1 KW amplifiers in use on SOTA summits.

Some of the Chinese manufacturers now offer compact dualband (and even quadband) VHF/UHF transceivers that output 10 to 30 watts of RF power. I purchased the Tytera MD-8600 based on my experience with other Tytera products. The radio’s specified output power is 25 watts on 2 meters. The DC power current is rated as 0.2 A on receiver and 4A on transmit, not too bad for battery operation. I paired it with a 13.2V LiFe battery rated at 4300 mAH. In theory, that would provide over an hour of transmit time or 21 hours of receive. That should be plenty for the typical SOTA activation. The size is a slightly larger than 4″ W x 1.5″ H x 5″ D and it weighs about 2 pounds. All in all, this setup is very compatible with the typical backpack portable operation.
Let’s do a little math to understand the difference in transmit signal. The TH-8600 puts out 25W compared to the 5W from FT-60. The difference in dB is 10 log (25/5) = 7 dB. Someone said to me “hey, that’s only a little more than one S unit, which is normally defined as 6 dB. Is that really enough to make a difference?” To which I responded, “yes, 7 dB can make the difference between making the radio contact or not…when signals are near the noise floor of the receiver.” For strong signals, it just doesn’t matter.
I’ve used this configuration on three SOTA activations and I like the results. On two of the activations, I compared the TH-8600 (25W) to the Yaesu FT-60 (5W) that my hiking partner (Joyce/K0JJW) was using. Both radios were connected to 1/2-wave vertical antennas, operating on 2m FM. The radios performed the same on receive, as expected. But the weaker stations we were working had trouble hearing the FT-60. Again: if signals were strong, it didn’t matter but the extra power made the difference when near the noise floor.
I checked out the basic performance of the radio on my test bench and found it to be adequate. The transmit frequency was spot on, the harmonics and spurious on 2m were about 60 dB below the carrier. The receiver sensitivity was about 0.2 microvolts. The RF output power was low, 22.4 W on 2m and 17.7W on 70cm (compared to the specs at 25W and 20W).
I was hoping the receiver performance would be better with regards to rejecting adjacent channel signals and intermodulation. I don’t have a good test bench for that but I can tell you that I noticed some unwanted interference from transmitters that were not close to my location.
How Many dB’s Is That?
So let’s summarize the dB situation.
5W HT with standard rubber duck antenna 0 dB 5W HT with 1/2-wave antenna +8 dB 3-element Yagi antenna (Arrow or similar) +6 dB 25W transceiver (vs 5W output) +7 dB Total improvement (25W with yagi vs HT) +21 dB
Wow, I can improve my signal strength by over 20 dB be making these improvements! I should point out that the antenna improvements help on both transmit and receive, while the increased transmit power only improves your stations transmitted signal.
73, Bob K0NR
The post More Power For VHF SOTA appeared first on The KØNR Radio Site.
 Twenty Six SOTA Summits
Twenty Six SOTA Summits
 I’ve written before about how operating goals can be a good motivator for getting on the air and making ham radio contacts. It is fun to have a goal to work towards and keep checking items off on the list. A few years ago, I decided to apply this approach to Summits On The Air (SOTA). SOTA is ripe for this kind of thing, given its extensive database and tracking of QSOs.
I’ve written before about how operating goals can be a good motivator for getting on the air and making ham radio contacts. It is fun to have a goal to work towards and keep checking items off on the list. A few years ago, I decided to apply this approach to Summits On The Air (SOTA). SOTA is ripe for this kind of thing, given its extensive database and tracking of QSOs.
Our family has a cabin in the mountains that we use to hike, jeep, ski, snowshore, explore, escape … So I decided to make a list of the SOTA summits in the general vicinity of the cabin. I did not use a precise criteria, just listing the summits that seemed close by. I used the Lists Of John web site as a tracking tool. That site is used by hikers/climbers to track their ascents, often working on their own list of summits based on whatever criteria that interests them.
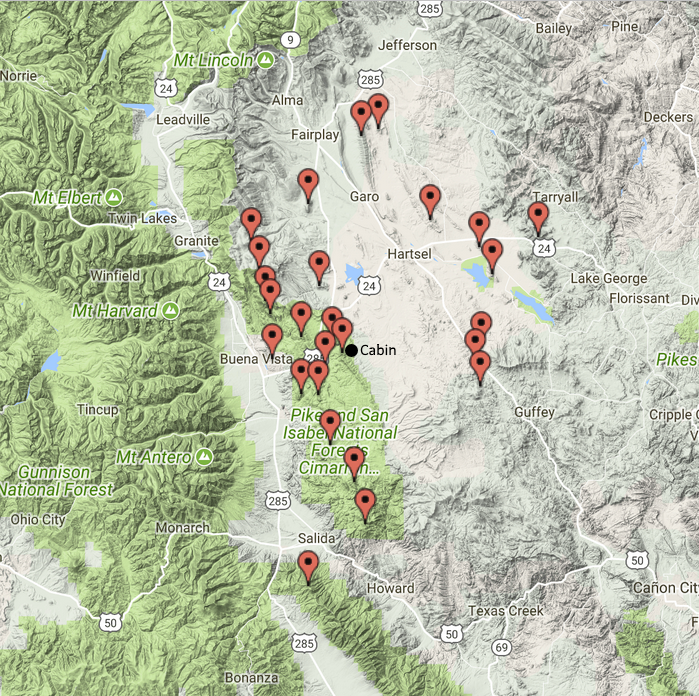 This list turned out to have 26 summits on it and I completed the last one a few months back, which was an unnamed peak (W0C/SP-055). Fifteen of these were the first activations of those summits. Some of these have still not been activated by anyone else (except for Joyce K0JJW, who usually hikes with me).
This list turned out to have 26 summits on it and I completed the last one a few months back, which was an unnamed peak (W0C/SP-055). Fifteen of these were the first activations of those summits. Some of these have still not been activated by anyone else (except for Joyce K0JJW, who usually hikes with me).
Now that I have completed that list, I obviously need to create a new one. With all of the SOTA summits available in Colorado, I won’t run out of options any time soon.
73, Bob K0NR
The post Twenty Six SOTA Summits appeared first on The KØNR Radio Site.
 TyMD380tools for Tytera MD-380
TyMD380tools for Tytera MD-380
 The Tytera MD-380 is an low cost radio for analog FM and DMR on the 70cm band (see video here). One of the limitations with the radio is that it only holds 1000 contacts…which seems like a lot of contacts but it fills up quickly. With DMR, each radio or user has a unique 7-digit radio ID number. For ham radio use, the DMR-MARC organization maintains a database that maps radio ID number to user name and callsign. If a user is in your contact list, the user’s name and callsign pops up in your radio’s display. Otherwise, you just see the radio ID which is not very helpful. There are over 63,000 users in the database with more being added on a daily basis.
The Tytera MD-380 is an low cost radio for analog FM and DMR on the 70cm band (see video here). One of the limitations with the radio is that it only holds 1000 contacts…which seems like a lot of contacts but it fills up quickly. With DMR, each radio or user has a unique 7-digit radio ID number. For ham radio use, the DMR-MARC organization maintains a database that maps radio ID number to user name and callsign. If a user is in your contact list, the user’s name and callsign pops up in your radio’s display. Otherwise, you just see the radio ID which is not very helpful. There are over 63,000 users in the database with more being added on a daily basis.
There are a number of firmware updates to the MD380 and I have not checked them all out. I heard some guys talking about the TyMD380Tools on one of the DMR talkgroups, so I decided to give it a try. This software was developed by KG5RKI (go here) and is easily installed from Windows without a lot of messing around. This firmware upgrade loads the entire DMR-MARC database into the radio.
Now that I have the worldwide database of DMR users loaded onto the radio, its like having caller ID on my HT (see photo below). Actually, its better than that, it pulls up the other ham’s full name, callsign and location information.
 This may not seem like a big deal but I’ve found it to be surprisingly useful. I am often scanning a few channels or talkgroups with my radio and just listening casually. I may not be tracking who’s talking but I can just look at the radio to see who’s on the air. It’s one of those convenience features that makes me think “why don’t all of my radios do this?”
This may not seem like a big deal but I’ve found it to be surprisingly useful. I am often scanning a few channels or talkgroups with my radio and just listening casually. I may not be tracking who’s talking but I can just look at the radio to see who’s on the air. It’s one of those convenience features that makes me think “why don’t all of my radios do this?”
The TyMD380Tools implements a bunch of other features but increasing the number of contacts has been the most important one for me. This is a great example of radio amateurs adapting (“hacking”) commercial gear with improvements for ham radio use. KK4VCZ, DL4YHF and others contributed to this code. Check out the software…seems to work great.
73, Bob K0NR
The post TyMD380tools for Tytera MD-380 appeared first on The KØNR Radio Site.












