Author Archive
 This Spewed Out of the Internet #29
This Spewed Out of the Internet #29
 More important
More important information insight stuff spewing forth from the interwebz:
The actor Tim Allen, who’s character on the TV show Last Man Standing is a ham radio operator, recently received his Technician License. According to Wikipedia, Allen holds the callsign KK6OTD under the name Tim Dick.
The FCC says that Marriott has been interfering with their customers’ use of WiFi hotspots at the Gaylord Opryland Hotel and Convention Center in Nashville, Tennessee. It seems that they wanted to “encourage” customers to pay for WiFi service.
ICOM has made available some cool amateur radio guides on their web site, including a World Map, USA Band Plan Chart and a USA VHF Grid Map. Oh, ICOM, please note that those grid locators are not actually “squares.”
Those Ham Hijinks guys must have bought a new ribbon for their typewriter since they’ve cranked our these articles: Obama Signs Ham Radio Executive Order and Man Creates Multi-Purpose Rotator.
Over at HamRadioSchool.com, I added another Shack Talk article, this one about ham radio awards: Operating Awards: Chasing Wallpaper.
73, Bob K0NR
 Mt Herman: SOTA plus VHF Contest
Mt Herman: SOTA plus VHF Contest
The North America SOTA Weekend coincided with the ARRL September VHF Contest, which I interpreted as a great opportunity to do a combination SOTA activation and QRP VHF operation. A few other folks thought that was a good idea so we all got on the air from SOTA peaks on the Sunday of the weekend. I decided to operate from Mount Herman (W0C/FR-063) in grid DM79. I hiked up the same mountain for last year’s September contest and got soaked by the rain. Fortunately, the weather was excellent this year, making it a great day.
For radio equipment, I took a couple of HTs for 2m and 70 cm FM and the FT-817 for CW/SSB on 6m, 2m and 70 cm. Most of the SOTA action would be on 2m FM but SSB is critical for working the VHF contest. I did put out the word to the usual VHF contesters that there would be FM activity and did work a few of them via 2m FM. The 2m FM calling frequency, 146.52 MHz, is commonly used for SOTA but is not allowed for contest use. (Another example of how this rule is just a barrier to contest activity.) We used 146.55 MHz for the contest contacts.  I had coordinated with Brad WA6MM who was going to be on Grays Peak (W0C/FR-002), one of the Colorado 14ers. When he made the summit, I had my 2m yagi antenna pointed in his direction and easily worked him on 2m FM at a distance of 65 miles. Brad was using an HT with a 1/2-wave vertical antenna. Also, I worked Stu W0STU and Dan N0OLD on Bald Mountain (W0C/FR-093) , which sits on the east side of I-25 right at Monument Hill. Contest activity was light, as usual for the September contest in Colorado. We did have two rover stations that activated a few of the unpopulated grids in eastern Colorado: George AB0YM and Jonesy W3DHJ.
I had coordinated with Brad WA6MM who was going to be on Grays Peak (W0C/FR-002), one of the Colorado 14ers. When he made the summit, I had my 2m yagi antenna pointed in his direction and easily worked him on 2m FM at a distance of 65 miles. Brad was using an HT with a 1/2-wave vertical antenna. Also, I worked Stu W0STU and Dan N0OLD on Bald Mountain (W0C/FR-093) , which sits on the east side of I-25 right at Monument Hill. Contest activity was light, as usual for the September contest in Colorado. We did have two rover stations that activated a few of the unpopulated grids in eastern Colorado: George AB0YM and Jonesy W3DHJ.
Band QSOs X pt = QSO pts. X Grids = Points ----------------------------------------------------------- 50 8 1 8 5 40 144 23 1 23 5 115 432 14 2 28 3 84 ----------------------------------------------------------- TOTALS 45 59 13 767
My contest score was not bad for a few hours of operating QRP portable. It turns out that I had set the Colorado section record for “single-op portable” back in 1990 with just 624 points (using my old callsign KB0CY). Oddly enough, 24 years later it appears that I set a new record. (This speaks more to the lack of QRP activity during the September contest and less about my incredible operating ability.)
All in all, it was a great day in the mountains to take a hike and play with radios. I will probably do the SOTA + VHF Contest activation again.
73, Bob K0NR
 Portable All-Mode VHF Radio: FT-817 vs KX3
Portable All-Mode VHF Radio: FT-817 vs KX3
For truly portable mountaintop all-mode VHF operating, especially SOTA and VHF contests, the Yaesu FT-817ND has been my rig of choice. You might say that it is really the “only game in town” for a 6m/2m/70cm radio that fits in a backpack.
I’ve had my eye on the Elecraft KX3 transceiver ever since it was introduced, but really I have been waiting for the 2m module to become available. (The KX3 has HF plus 6m standard.) After being announced over a year ago, the 2m module is now shipping and radio amateurs are getting their hands on the unit.
I do enjoy getting on the HF bands but my radio passion has always been centered on 50 MHz and higher. For my purposes, the manufacturers could have left off the HF bands and just designed a portable rig that does 6m, 2m and 70 cm (and maybe 1.25m, too). Or how about a dualband HT that does SSB?
I’ve used my 817 for many portable operations, so I have quite a bit of stick time on that rig. I’ve not really used a KX3, other than to play with it at hamfests. I’ve also talked with a number of KX3 owners that really like the rig. I was a bit surprised that the KX3 power is only 2.5W minimum (3W typical), compared to 5W with the FT-817. (Yeah, I know, that’s only 3 dB difference, blah, blah, blah.) One of the big complaints on the 817 is that it is a bit of a battery hog on receive (450 mA) but the KX3 is not that much better at 300 to 350 mA. Here’s my comparison table for the two radios — with the emphasis on VHF operation.
| FT-817ND | KX3 with 2m Module | |
| Bands | HF + 6m, 2m, 70cm | HF + 6m, 2m |
| 6m Power Out | 5W | 8W |
| 2m Power Out | 5W | 2.5 -3W |
| Standby rx current (2m) | 450mA | 300 to 350 mA |
| Transmit current (2m) | 2A | 1.7A |
| Weight | 2.5 lbs, 1.2 kg | 1.5 lbs, 0.7 kg |
| Price | $690 | KX3 assembled $900 Hand mic $60 2m module $260 Total: $1220 |
The price comparison is a bit tricky because the KX3 can be purchased in kit form for $100 less. Many hams will actually see the kit assembly as a plus, since they get the satisfaction of building their own radio. A microphone is not standard on the KX3, so I added that to the list. Also, there are several different variations on the 2m module, depending on whether the automatic antenna tuner for HF is installed and whether the factory installs the option. I just picked a price that was in middle of the range.
The table would lead you to conclude that the FT-817ND is the clear winner mostly based on price (and the 70cm band). But its not that simple. There is a lot to like about the KX3, including the nice big display and the trail friendly layout. It also has more features for CW, PSK31 and RTTY.
For me, the answer is clear: keep on keepin’ on with the 817, since there is not enough of an advantage to go to the KX3. But I will probably keep lusting after it anyway. This also raises the question: what does Yaesu have coming to replace the aging 817?
What do you think?
73, Bob K0NR
 SOTA Summit Activation: Sandia Crest (W5N/SI-001)
SOTA Summit Activation: Sandia Crest (W5N/SI-001)
Joyce KØJJW and I were headed to the Duke City Hamfest in Albuquerque when we decided to make a side trip up Sandia Crest for a low overhead (read: slacker) Summits On The Air (SOTA) activation.
Sandia Crest pokes up 10,678 feet, towering over Albuquerque at roughly 5000 feet. Although the weather was rainy, we enjoyed the drive up the paved Sandia Crest Road through the Cibola National Forest. This looks like a great area to explore and we’ll probably be back sometime in the future.
At the parking lot, about 40 vertical feet below the summit, we paid the $3 per day use fee (self-service USFS station), grabbed the radio gear and headed up the walkway to the top. There is a gift shop and restaurant at the south end of the parking lot, along with several hiking trails. A large radio site on the north end of the parking lot has numerous towers and high power transmitters. The field strength is so strong that a sign has been placed there to warn of radio interference to car alarms and keyless remotes.
I pulled out the trusty Yaesu FT-60 handheld transceiver with the MJF-1714 1/2-wave antenna for 2 meters. I gave a few calls on 146.52 MHz and heard no replies. I am thinking, “surely with so many hams in town for the hamfest, someone is listening on five two.” Joyce was standing next to me with her FT-60 and a rubber duck antenna. We noticed that her radio was hearing signals that I could not hear.
Hmmm, the radio with the better antenna is not able to hear anything but the radio with a crummy rubber duck is working fine. At this point, I realized that my HT was being overloaded from the transmitter site with my high-efficiency antenna doing a great job of coupling those signals into my radio. I had to chuckle about this since I’ve often pointed out the poor performance of your typical rubber duck antenna. In this case, the less effective antenna was doing us the favor of reducing interference.
I swapped antennas and began making calls on 2m fm with the rubber duck. I also moved further away from the radio site to reduce the signal level. Yep, now I heard some guys coming back to me on 146.52 MHz. I could tell there was still some interference but it was workable. In short order, I had these stations in the log: KE7WOD, W5AOX, K5LXP, WB5QXD and K0JJW (after moving downhill outside of the activation zone),. Thanks for the QSOs!
I will admit that NM5SW mentioned the interference problems on this peak, so I had fair warning. Keep in mind that the FT-60 has reasonably good intermod performance, probably better than your average HT, and was getting completely blocked with the long antenna. I was glad that I was not using one of the Baofeng HTs. It made me wonder how well my FT-817 would do under the same conditions, but that will be a test for another day.
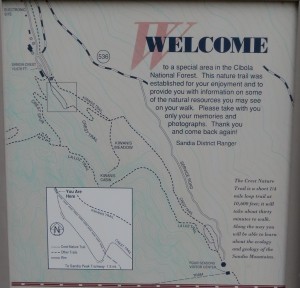
Another way to ascend the peak is via the Sandia Peak Tramway, which comes up from the Albuquerque side. We came across this sign that shows the trail system near the summit and indicates the top of the tram (click to expand). The tram drops passengers off some distance from the actual summit, so you’ll have about a 1.5 mile hike to the summit.
In summary, it was a successful activation although the weather could have been better. The big thing I learned was that a more efficient antenna is not always the best antenna. Sometimes a crummy rubber duck does better!
73, Bob K0NR
P.S. I later heard from Mike KD5KC that the Kiwanis Cabin (shown on the map) is a good place to operate from without radio interference issues on HF and VHF.
 SOTA Summit W0C/SP-042 Activation
SOTA Summit W0C/SP-042 Activation
For the 2014 Colorado 14er Event, Joyce K0JJW and I decided to try a summit close to our cabin near Trout Creek Pass. The basic idea was to activate a non-14er SOTA peak with good VHF paths to all of the Colorado mountains. We also wanted to demonstrate the idea of activating Summits On The Air peaks during the 14er event.
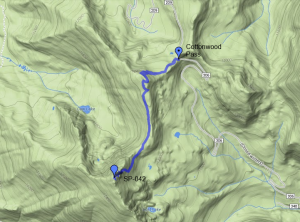
We chose an unnamed peak (W0C/SP-042) that rises to 12,792 feet near Cottonwood Pass . This summit was already on my list of SOTA peaks to activate, so that was another plus. The trail starts at Cottonwood Pass, right on the continental divide and runs along the divide for about 2 miles.
In fact, we followed the Continental Divide Trail (CTD) to get to this SOTA peak. I’ve done several backpack trips on the CTD and its always a blast to be walking along the top of the continent enjoying the awesome views.
The main trail passes over the top of another summit at 12,400 feet before continuing on to SP-042. The trail does not go to the top of SP-042, passing it on the east side. We just stayed on the trail until we were due east of the summit, then climbed up the east side which turned out to be a bit steeper than it looked. On the way down, we left the summit by following the ridge a bit to the south and found a gentler route back to the trail. Also on the way back, we followed a side trail to the east of the 12,400 foot summit, saving some vertical gain and loss. My GPS app on the iPhone logged the one-way distance as 2.2 miles (including going over the first summit). It looks shorter on the map but the switchbacks add some distance.
After we reached the summit around 9 am, I quickly assembled the 2m/70cm Arrow antenna and mounted it on my hiking stick. Once I had the FT-817 up and running, I spotted myself on Sotawatch.org using the SOTA Goat app. Logging was done with HamLog on my iPhone.
I worked a number of mountaintop stations on 2m fm (147.42 and adjacent simplex frequencies) with the best DX being N4MMI on Redcloud Peak, about 80 miles away. I tried calling on 2m and 70 cm SSB without any luck. Joyce made a few contacts on 446.0 MHz using an HT with a vertical antenna.
The weather cooperated all morning with mostly white fluffy clouds. We stayed on the summit until noon and then hit the trail back to the pass. This hike is now one of our favorites, really good for visitors that want a taste of hiking above treeline with great views.
73, Bob K0NR
 This Spewed Out of the Internet #28
This Spewed Out of the Internet #28
 More important
More important things have spewed forth from the interwebz:
HamRadioNow interviews the Ham Hijinks guys and has the nerve to actually publish the video. Later the Hijinks crew posted this article about changes being made to Field Day.
Baofeng is going to change its name. Or is this just another Ham Hijinks article?
WE2F writes: 146.52 Reasons to Monitor VHF Simplex but whatever you do, do not use 146.52 MHz on Field Day. Mike AD5A posts Why Operate QRP from Summits? The FCC kicks the butt of a cell phone jammer manufacturer, to the tune of $34.9M and also fines a couple of 14.313 MHz problem children.
A Broadband Over Powerline (BPL) provider bites the dust. Did I mention that it is a really dumb idea to transmit bits over AC power lines?
I did a little explaining about those antenna connectors on handheld radios. Randy (K7AGE) has a neat video showing some basic 2m FM portable operating.
I knew it: Digital is overrated and vinyl is making a comeback. Really.
Due to popular demand, I updated the VHF QRP page. Yes, some radio hams do operate QRP above 50 MHz…apparently for the same reasons that people operate HF QRP. Which is to say we really don’t know why.
I also found that the domain name for the Colorado 14er Event was broken, so I fixed it. See ham14er.org This event is the most fun you can have dorking around with radios in the Colorado mountains. Also, be sure to check out these operating tips.
73, Bob K0NR
 Announcing the October 2014 WØTLM Technician License Class
Announcing the October 2014 WØTLM Technician License Class
 Ham Radio Two-Day License Class
Ham Radio Two-Day License Class
Sat October 18 and Sat October 25 (8 AM to 5 PM) 2014
Location: Tri-Lakes Monument Fire Station 1, Monument, CO
The Technician license is your gateway to the world-wide excitement of Amateur Radio …
- Earn your ham radio Technician class radio privileges
- Pass your FCC amateur radio license exam right in class on the second day
- Multiple-choice exam, No Morse Code Required
- Live equipment demonstrations
- Learn to operate on the ham bands, 10 Meters and higher
- Learn to use the many VHF/UHF FM repeaters in Colorado
- Find out how to participate in emergency communications
There is a $25 registration fee for the class.
In addition, students must have the required study guide and read it before attending the two-day class: HamRadioSchool.com Technician License Course $20.95
(make sure you get the most recent edition of this book, updated for the new FCC exam questions)
Advance registration is required (no later than one week before the first session, earlier is better! This class usually fills up early.)
To register for the class, contact: Bob Witte KØNR
Email: bob@k0nr.com or Phone: 719 659-3727
Sponsored by the Tri-Lakes Monument Fire Radio Association
For more information on amateur (ham) radio visit www.arrl.org or www.wedothat-radio.org