Archive for the ‘antennas’ Category
 Working POTA: A beginner’s guide and video
Working POTA: A beginner’s guide and video
SARC in the park!
We had an interesting workshop on Saturday, September 16, 2023. 'SARC in the Park' was a presentation by Dmitry VA7DVO for our members interested in POTA activations. You will find more about getting started in POTA at their website, and in our free digital magazine 'The Communicator'.
With an easy to build and inexpensive segmented 5-band wire dipole antenna, we made several of the 17m SSB POTA contacts shown in this video, including Switzerland, Italy and with a mobile station in Northern England.
The antenna plan is at: https://bit.ly/SARC23Sep-Oct on page 45.
Alex VA7PVC, Dmitry VA7DVO , and Leandro VE7LSI at Serpentine Fen
Here is the presentation on video and a look at the activation
https://youtu.be/RTAKs40DHjQ
Do you want to know what else is happening at SARC?
 New Antenna: The Following Footprints Are of My CW Signals (2021-March-14 @ 04:00 to 04:20 UTC).
New Antenna: The Following Footprints Are of My CW Signals (2021-March-14 @ 04:00 to 04:20 UTC).
The following footprints are of my CW signals on 2021-March-14 at about 04:00 to 04:20 UTC.
Click on this image to see a larger version of this image:
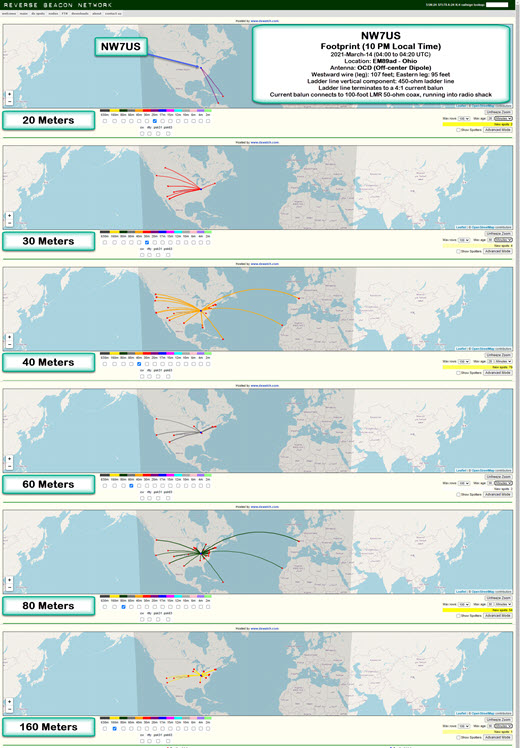
Location: EM89ad – Ohio
Antenna: OCD (Off-center Dipole)
Description of Antenna:
This is an off-center dipole, with the two legs running East-East-South (approximately 125 degrees of North), and West-West-North (about 306 degrees on the compass). The westward wire (leg) is approximately 107 feet in length, while the eastward leg is about 95 feet in length.
These legs (an off-center-fed dipole) is directly connected to about 90 feet of 450-ohm ladder line, which is hanging directly below, vertically, the feed point. The feed point is 50 feet above the ground.
The ladder line terminates (at the 12-feet-above-ground point) to a 4:1 current balun. This current balun then connects to a 100-foot LMR 50-ohm coax, which is running into the radio shack. It is connected via an antenna switch to my Icom IC-7610 transceiver. I am transmitting a 100-watt CW signal using an Icom IC-7610, in the following format:
TEST TEST TEST DE NW7US NW7US NW7US
The Reverse Beacon Network reports any spotting of this test transmission. The beta mapping interface, at http://beta.reversebeacon.net/main.php, then maps the resulting spots. To learn more about the RBN, visit http://beta.reversebeacon.net/index.php, or, http://reversebeacon.net/index.php.
I show the 20-, 30-, 40-, 60-, 80-, and 160-Meter band footprints.
I’ve been capturing these CW transmission spots, at different times of the day, today. I’ll get data from several days, at regular intervals, and create a overview of how the antenna appears to be working during this month and under these propagation conditions.
73 de NW7US dit dit
..
 BCB DX + A (Possibly) Quieter Receive Antenna
BCB DX + A (Possibly) Quieter Receive Antenna
The earlier very quiet geomagnetic field has produced some amazing propagation on the AM Broadcast Band for west coast DXers. Where local blowtorches don't splatter the band, the past few nights have produced audible signals from several European countries while the mornings are filled with Asians and signals from Alaska ... yes, on the AM Broadcast Band!
The morning of October 11th was particularly good here, with 9 different stations in Alaska heard. Listen and see if you can hear the identification at the top of the hour (7 AM my time):
780 KNOM Nome https://qsl.net/ve7sl/knom.mp3
670 KDLG Dillingham https://qsl.net/ve7sl/kdlg.mp3
700 KBYR Anchorage https://qsl.net/ve7sl/kbyr.mp3
680 KBRW Barrow https://qsl.net/ve7sl/kbrw.mp3
890 KBBI Homer https://qsl.net/ve7sl/kbbi.mp3
This is a short clip from HLAZ, Far East Broadcasting Company, with their 'Radio Liangyou' program in Japanese. HLAZ is located in Jeju, South Korea. They will also respond to reception reports with a nice card ... sadly a growing rarity with AM broadcasters nowadays.
These were received using my Perseus SDR and 10' x 20' active loop pointed to the NW.
Hopefully these nice conditions will continue for some time but on the other hand, I'd like to see the Sun ramp-up its sunspot production as fast as it can, which would likely put a damper on these quiet conditions. (post edit: and that's exactly what happened!)
An interesting antenna that may help overcome their noise issues is described by KK5JY on his website here.
It looks simple enough to deploy and try to see if it overcomes your local noise issues. Those with underground utilities however, may find that it makes the noise worse.
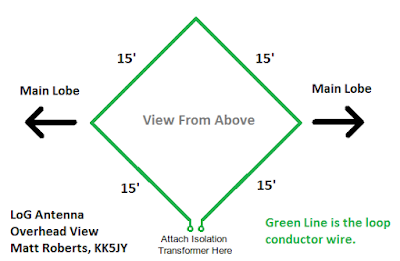 |
| courtesy: kk5jy.net |
 Just Get On The Air! (A Makeshift Temporary Dipole Shortwave Antenna)
Just Get On The Air! (A Makeshift Temporary Dipole Shortwave Antenna)
It might not take as much antenna as you may think would be necessary to make two-way contacts on shortwave radio (as an amateur radio operator putting an HF transceiver on the air). However, often, makeshift antennae are effective enough to be viable–just look at all the contacts many amateur radio operators make with their low-power (QRP) rigs (transceivers) using short, helically-wound, mobile antenna sticks. If they can work magic with such inefficient antenna setups, surely your effort at an antenna would pay off to some degree. Right?
[embedyt] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-k5Su–ez2Y[/embedyt]
Of course, I want to make a proper dipole out of this example antenna. But, while I wait for the rest of the parts I need to complete this antenna project (pulleys and a ladder, and maybe a potato launcher), I’ve put this makeshift antenna on the air, with it just high enough so that I can enjoy some time on the shortwave bands.
With this antenna, I’ve made successful two-way voice and Morse code contacts (QSOs) with stations in Europe and across North America. I am able to tune it on the 60-, 40-, 30-, 20-, 15-, 17-, 12-, and 10-Meter bands. Reverse beacon detection picks up my Morse-code CW signals, especially on 40 meters (the band on which it is tuned physically).
The bottom line: just get something up in the air and start communicating. Improve things over time. You’ll have much fun that way.
73 de NW7US dit dit
 Software-Defined Radio: Try Before You Buy? You Might Like It!
Software-Defined Radio: Try Before You Buy? You Might Like It!
Sure! You don’t need to have a software-defined radio (SDR) before you start learning how to use the technology; there are a few different paths you can take, exploring and learning about SDR.
One way to gain some experience with SDR without spending a dime is to install a free software package for the very popular, non-Linux, operating system (that starts with ‘W’), and give SDR a test drive. If you like it, you might consider getting your own hardware (like the SDRplay RSPdx, for instance), and connecting it up to your computer and running this software, too.
Why I Dived Into SDR
I have always loved radio, ever since the early 1970s, when I discovered shortwave radio. In the last couple of years, I’ve had an increasing interest in the world of SDR. When I am working, but away from home (remember those days, before Covid?), I want to sample news and programming from around the world, but through shortwave. The way to do that, I found, is by using the various SDR options which allow a person to tune a remote receiver, and listen.
I also find working with the waterfall of a typical SDR-software user interface rewarding because, instead of blindly searching for signals in a subband, I can see all of the received signals on the scrolling time representation of a slice of frequency. Simply select that signal on the waterfall, and the radio tunes right to it.
I often connect to different SDR radios around the world, to catch all manner of shortwave signals, from maritime, military air, trans-oceanic air, or coast guard radio traffic, or other interesting HF communications including amateur radio CW and SSB signals. Occasionally, I also check out VHF and UHF signals from around the world. All of that, while instead an office building that is not suited for shortwave radio reception.
I’ve now decided to give back to the community; I’ve added my SDR receiver to the collection of receivers located around the world on the SDRSpace network of SDR radios.
My new SDRplay RSPdx software-defined radio receiver is live, via http://www.sdrspace.com/Version-3, using the SDR Console software (Version 3).
The receivers are online whenever I am not transmitting and when there are no local thunderstorms.
Antenna Port A is connected to a wire antenna (a horizontal 100-foot wire that runs out from my house’s chimney to a tall tree; about 10 feet of that wire is oriented vertically, where the wire passes through a pulley and then is weighted down so it can move with wind-driven tree movement), while Antenna Port B is connected up to a VHF/UHF discone.
Both antenna systems have an AM Broadcast band notch (reject) filter reducing local AM Broadcast-Band radio station signals by about 30 to 40 dB. I need to use these because the very close KLIN transmitting tower is just miles away and those signals overwhelm the receiver. When I use the signal filters, the local AM Broadcasting signals no longer overwhelm the receiver.
In the following video, I first explain my SDR setup, and in the second half of the video, I tune around the radio spectrum, using the software to control my SDR receiver.
[embedyt]https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DHj917E1bKA[/embedyt]
A Couple of Questions
After watching this video, WO9B wrote an email to me. Michael asked of me two questions, summed up as:
1. Your SDR window has the IF screen on top. How is that accomplished?
2. Your AM Broadcast filters; more info, please. I live in the area of mucho broadcast stations and that looks like something I could use.
In the following video, I demonstrate how I changed my layout of the SDR Console software. And, I mention the AM Broadcast Filter for SDR Receivers (the hardware filter is found here: https://g.nw7us.us/3kU5SJN).
[embedyt]https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YLBLHi441Zg[/embedyt]
To Use My Receiver
Download the latest version of SDR-Console from https://www.sdr-radio.com/download – there is a 32-bit and a 64-bit Windows installation package.
The 64-bit installation package may be downloaded from one of these three sources:
1. Google: https://g.nw7us.us/3auBq44
2. DropBox: https://g.nw7us.us/310ooIG
3. Microsoft: https://1drv.ms/u/s!AovWaZDu7Hrd3U-yqK1bs3wuaFw2?e=o4nKeh
The 32-bit installation package can be downloaded from one of these three sources:
1. Google: https://g.nw7us.us/3iLasrZ
2. DropBox: https://g.nw7us.us/3g4VcVc
3. Microsoft: https://1drv.ms/u/s!AovWaZDu7Hrd3U4mJiiRtI9lm70s?e=HDG4ZX
Install the SDR Console package according to the directions given. Once you have the software installed, you will want to add my server. It takes some work to get familiar with the software, but there are online FAQs on how to begin.
One guide on how to add a server to the list from which you can pick may be found, here:
https://www.sdrplay.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/02/SDRConsoleV3-ServerGuide1-1.pdf
I worked on getting all of the bugs worked out of my installation before making the video. It did take some work, and reading up on things. But, the software is solid and a good contender against SDRuno, and HDSDR, and, this way I can share it online with you.
My server is known as, ‘0 NW7US‘ — it will be online when I am not using my antenna systems for transmitting. It will be offline during thunderstorms, or during times when I must use the systems for transmitting.

Software-defined radio is a great way to hear all sorts of communications, from local AM broadcast stations, FM stations, VHF Air Traffic, to shortwave radio stations including amateur radio HF communications.
Thank you for watching, commenting, and most of all, for subscribing; please subscribe to my YouTube Channel: https://YouTube.com/NW7US Also, please click on the bell, to enable alerts so that when I post a new video, you will be notified. By subscribing, you will be kept in the loop for new videos and more.
73 de NW7US
.. (yes, this is an expansion of an earlier post… forgive the redundancy… thank you) ..
 Check Out My New SDRplay RSPdx Software-Defined Radio Receiver – Live!
Check Out My New SDRplay RSPdx Software-Defined Radio Receiver – Live!
My new SDRplay RSPdx software-defined radio receiver is live, via http://www.sdrspace.com/Version-3, using the SDR Console software (Version 3).
The receivers are online whenever I am not transmitting and when there are no local thunderstorms.
Antenna Port A is a wire antenna (100′), while Antenna Port B is a VHF/UHF discone. Both have an AM Broadcast band reject filter, reducing local AM Broadcast signals by about 30 to 40 dB. I need to use these because the very close KLIN transmitting tower is just miles away and those signals overwhelm the receiver. When I use the signal filters, the local AM Broadcasting signals no longer overwhelm the receiver.
Let me know what you think. Enjoy!
To use my receiver:
Install the latest version of SDR-Console which can be downloaded from https://www.sdr-radio.com/download
Install SDR Console according to the directions given. Once you have the software installed, you will want to add my server.
It takes a little to get familiar with the software, but there are online FAQs on how to begin.
My server is known as, ‘0 NW7US‘ — it will be online when I am not using my antenna systems for transmitting. It will be offline during thunderstorms, or during times when I must use the systems for transmitting.
Software-defined radio is a great way to hear all sorts of communications, from local AM broadcast stations, FM stations, VHF Air Traffic, to shortwave radio stations including amateur radio HF communications.
Thank you for watching, commenting, and most of all, for subscribing; please subscribe to my YouTube Channel: https://YouTube.com/NW7US Also, please click on the bell, to enable alerts so that when I post a new video, you will be notified. By subscribing, you will be kept in the loop for new videos and more.
Video:
[embedyt] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DHj917E1bKA[/embedyt]
73!
 PAØRDT Miniwhip Shakedown
PAØRDT Miniwhip Shakedown
***********************************
A recent posting to the 'ndblist group' by Mike, an ardent NDB DXer in the UK (Sussex), announced the recent completion of his four-part video series describing the installation and testing of a new PAØRDT active antenna.
 If you may be contemplating the installation of an active antenna such as this, or perhaps making a start at DXing the NDB band or listening on 630m, then you might enjoy following Mike's journey as he demonstrates that living in the noisy suburbs need not keep you from enjoying the LF/MF bands. Mike includes some interesting tests involving his grounding system versus noise ingress and the results of keeping the electrical main's ground isolated (or not) from the antenna cable's ground.
If you may be contemplating the installation of an active antenna such as this, or perhaps making a start at DXing the NDB band or listening on 630m, then you might enjoy following Mike's journey as he demonstrates that living in the noisy suburbs need not keep you from enjoying the LF/MF bands. Mike includes some interesting tests involving his grounding system versus noise ingress and the results of keeping the electrical main's ground isolated (or not) from the antenna cable's ground. The PAØRDT active whip is available from PAØRDT himself or if you are handy with a soldering iron, you might choose to build the same antenna in your workshop. These simple yet highly effective receiving antennas are being used successfully by hundreds of listeners all over the world and for their size provide some pretty amazing performance.
Much more information on the PAØRDT e-probe antenna may be found here in a previous blog posting. To see more of Mike's videos, you can visit his interesting Youtube Channel here.