Amateur Radio Weekly – Issue 285
Amateur Radio Weekly – Issue 285
Bill to replace symbol rate limit reintroduced
Congresswoman Debbie Lesko introduced The Amateur Radio Communications Improvement Act on May 11.
ARRL
Enhanced SKYWARN system embraces GMRS
Made up of both Ham and GMRS repeater systems, Ham and GMRS clubs join forces.
Chattanooga Amateur Radio Club
Introducing NetFinder
The definitive Ham Radio net directory.
Midnight Cheese
A Ham Radio Memorial Day
Amateur Radio is not and should not be just about radio.
Off Grid Ham
RepeaterPhone [iOS App]
Connect to AllStarLink and Echolink repeaters from a single iOS app.
RepeaterPhone
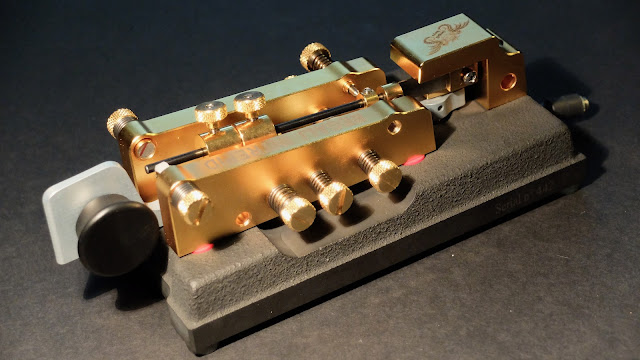
The Perfect Bug
No one needs a $580 key, but this is a very fine piece of engineering.
Ham Radio QRP
Tuned CW filter made from PVC pipe
It gives at least a 6 db boost at 700-800 Hz.
KE4GBE
Android tablet with a built in two way radio
136-174mhz, 400-490mhz DMR/FM – Embedded RTL-SDR.
RTL-SDR.com
Best bang-for-the-buck antenna ever
One of my best Ham-related purchases in 45 years.
AE5X
Video
Flying above downtown Seattle with Ham Radio operations
Flight over the majestic Seattle Skyline and Space Needle while conducting 2-meter FM radio operations.
W7NY
What Morse Code taught me
A view from a non-Ham.
Tortelikeatiger
License-free WinLink
Sending Winlink over license-free walkie talkies.
LB4HF
Get Amateur Radio Weekly in your inbox.
Sign-up here
Amateur Radio Weekly is curated by Cale Mooth K4HCK. Sign up free to receive ham radio's most relevant news, projects, technology and events by e-mail each week at http://www.hamweekly.com.
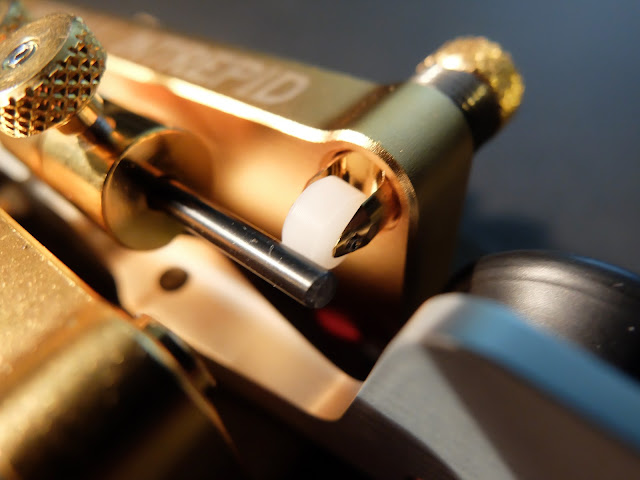
 Begali Intrepid
Begali Intrepid
The Perfect Bug?
A New Design
- The pendulum hinge is at the rear of the key rather than the middle
- The adjustments are all based on magnets rather than springs
- The dwell for the dits has a real control, rather than using various pieces of foam, string or clips to change dwell time
- The dit contact is a sprung plunger that always remains centered on the contact rather than brushing against it at various angles
- The split lever mechanism operates at the center of the key placing the DAH and DIT contacts much closer to one another than a traditional bug
- There is less mass in the pendulum itself than a Vibroplex Bug
- It has a sprung, nylon wheel damper that doesn't clatter
- It weighs a TON (well about 6 lbs) and feels welded to the desk without having to use non-slip material or using spit to semi glue them in place (yech, yes I use spit to hold my keys to my desk)
Preparing for Use
In Use
Conclusions?
Richard Carpenter, AA4OO, is a regular contributor to AmateurRadio.com and writes from North Carolina, USA. Contact him at [email protected].
 Three Tips for 2m FM SOTA
Three Tips for 2m FM SOTA

I do a lot of SOTA activating using 2m FM and have developed a few operating habits that can really make a difference. These may seem obvious but might be overlooked by operators new to the game. To get an overview of using VHF for SOTA, look at this article: How to Do A VHF SOTA Activation.
Here are three operating tips when using 2m FM for SOTA:
1. Upgrade Your Antenna
A handheld radio is commonly used for SOTA operation because it is a self-contained, compact radio. These radios always come with a rubber duck (electrically-short monopole) antenna. These antennas vary in quality but they are universally poor performers compared to a half-wave radiator. I’ve measured the effectiveness of many rubber duck antennas on 2 meters and they are somewhere between 8 and 12 dB worse than a half-wave radiator. So an easy upgrade is to use a half-wave telescoping antenna. Another popular option with a half-wave radiator is the roll-up J-pole (often called a “Slim Jim” antenna). An even better choice is a small 3-element Yagi such as the 146-3 from Arrow antenna, which is about 6 dB better than a halfwave antenna. Keep in mind that the Yagi should be held vertically-oriented for FM operating.
2. Open Your Squelch
The squelch circuit in an FM receiver requires the signal to be large enough to flip the squelch open. When operating at weak signal levels, the squelch may mask a signal that is actually readable. A recommended technique is to just open up the squelch control and let the FM noise come through. This maximizes the opportunity to pick out that weak signal out of the noise.
3. Point Your Antenna Everywhere
If you have a directional antenna, make sure you methodically point it in a variety of directions when calling CQ. For example, with a 3-element Yagi, you should divide up the 360 degrees around you into 45-degree sections. Point north, make a call, point northeast, make a call, point east, make a call, and so forth. Also be aware that the direct path to another station may not be the strongest path. This is especially true if you have tall summits around you that can block or reflect your signal. Many times I’ve pointed in the “right direction” to work another station but then found that the signals were strongest with the antenna pointed away from the direct path. So the secret is go ahead and try different antenna orientations to maximize the signal strength, even when you know the physical direction to the other station. Sometimes the radio waves decide to take another path.
Those are my three tips for today.
Do you have any to add?
73 Bob K0NR
The post Three Tips for 2m FM SOTA appeared first on The KØNR Radio Site.
Bob Witte, KØNR, is a regular contributor to AmateurRadio.com and writes from Colorado, USA. Contact him at [email protected].
 ICQ Podcast Episode 402- Rockall Dxpedition (MM0UKI)
ICQ Podcast Episode 402- Rockall Dxpedition (MM0UKI)
In this episode, we join Martin Butler M1MRB, Chris Howard (M0TCH), Martin Rothwell (M0SGL), Frank Howell (K4FMH), Bill Barnes (WC3B) and Leslie Butterfields (G0CIB) to discuss the latest Amateur / Ham Radio news, Colin Butler (M6BOY) rounds up the news in brief and in the episode's feature is MM0UKI Rockall Dxpedition.
We would like to thank our monthly and annual subscription donors for keeping the podcast advert free. To donate, please visit - http://www.icqpodcast.com/donate
- Artemis 2 Astronauts Flying to the Moon Could Phone Home with Ham Radio
- High-Altitude Balloon Launch
- Online Ham Bootcamp - 13th May 2023
- ARRL Support FCC Proposes Changes to 60-Metre Band
- UK Coronation Call Signs
- Air Travel Chaos Looms as US Leeps 5G Altimeter Refit Deadline
- Annual Armed Forces Day Crossband Test
- SSTV Transmissions from ORBICRAFT-ZORKIY
Colin Butler, M6BOY, is the host of the ICQ Podcast, a weekly radio show about Amateur Radio. Contact him at [email protected].
 Amateur Radio Weekly – Issue 284
Amateur Radio Weekly – Issue 284
DLARC Ham Radio library surpasses 75,000 items
Internet Archives Digital Library of Amateur Radio & Communications continues to expand.
DLARC
SSTV transmissions May 7-13
SSTV from ORBICRAFT-ZORKIY. Diplomas available upon receiving 3 of 6 images.
AMSAT
APRS Thursday
#APRSThursday is an APRS based net held each Thursday.
APRSPH
In the age of social media, Hams in Wyoming still use the airwaves
Besides connecting with people all over the world, operators also help out with emergency communications.
Cowboy State Daily
Preparing for ARRL Field Day
How are your coaxial cables looking these days?
OnAllBands
Students wanted for online Ham Radio course
NRAO is looking for 20 learners (18-20 years old) with an interest in learning about the electromagnetic spectrum and Ham Radio.
National Radio Astronomy Observatory
$30 Lowe’s Antenna
I went to Lowe’s and after wandering around, here’s what I came up with.
KB6NU
Listening to satellites: A journey with my RTL-SDR V3
A log of my personal journey with satellite RF.
Mohsen Tahmasebi
LoRa moon bounce
A group of students is taking the long range moniker to the extreme.
Hackaday
Is RG-8X the general purpose coaxial cable?
Signal loss may be a more significant limitation.
K0NR
Video
Radio off-grid from a cabin in Norway
Everything is either solar or generator powered.
LB4FH
Say hello to FreeDATA
Setting up FreeDATA, keyboard-to-keyboard chat over RF.
K5YVY
Blowing up capacitors
Gav and Dan overload some capacitors and film the explosive results at 187,500 fps.
The Slow Mo Guys
Get Amateur Radio Weekly in your inbox.
Sign-up here
Amateur Radio Weekly is curated by Cale Mooth K4HCK. Sign up free to receive ham radio's most relevant news, projects, technology and events by e-mail each week at http://www.hamweekly.com.
 Here we go again………
Here we go again………
September last year I had an issue with my Icom 7610, it was shutting down and restarting. The issue was a supply low voltage situation. With the 7610 if the incoming voltage drops below 11.44 volts the radio turns off. This voltage drop happens during transmit (CW in my case) then the radio cycles off, the current draw stops and the voltage goes back up and the radio cycles back on again. This is a normal situation with the 7610 and is supposed to happen with a voltage drop at or below 11.44 volts DC. In my last post when this happened in September 2022 I narrowed it down to the Anderson power pole connectors for more details click the "In my last post link above.
On Wednesday I was taking part in the 1-hour CWops mini contest and out of the blue while transmitting my 7610 cycled off and then on again. I thought "Here we go again". I had a good idea where the problem was and to finish the contest I lowered my power from 100 watts to 50 watts. I have the Astron SS-30M power supply and for some reason beyond me, Astron decided to use screw-down terminals to connect your radio DC cables. It is a small slotted screw and to me just a problem waiting to happen. My old Astron power supply had studs with nuts and made a very solid connection. There is a new version of the Astron SS-30 and it offers Anderson connections on the front. But the screw type connections are still present on the back of the supply.
I decided it was time to do 2 things remove the inline automobile fuse holder and fuse on both the DC positive and negative radio cables supplied by Icom. It has been documented many times how these fuse holders have caused issues with voltage drop due to a poor connection over time. The other thing was a bit more ambitious which was to remove the screw-down positive and negative terminals on the Astron power supply. They were to be replaced with studs and nuts for a solid connection. 
Old screw terminals
The Astron power supply is out of warranty as for sure doing this mod would certainly void the warranty. So lets get started....The screws fastening on the cover of the power supply are Torx-type screws and you will need the proper tool to get the cover off. Once the cover was off I removed the positive and negative cables from the back of the screw-type connectors. These 2 connectors were removed from the power supply and put in their proper place.....the garbage! 
Out to the trash!
Two holes now had to be drilled in the case for the new studs and this is where success and disaster are a very fine line from one another. I placed tape on the inside and outside of the case as fewer filings from the drilling make their way into the power supply case. I also placed some protection on the inside of the power supply to also catch filings. I then marked off the holes and I used 3 drill bits to slowly move the hole up to the 3/8 size I was looking for. A word about the drill bits, I put a large amount of tape around the bit where I wanted it to stop once the hole was completed. No matter how good you are once that drill bit makes it way through the metal case it is going to want to keep going. You have a lot of pressure on that drill and well no one's reflexes are that good. I use the tape as a drill stop and it worked just fine as no damage was done to the parts in the power supply.
Drill bits
I used fibre inserts in the holes to insulate the studs from the case. These came from my other 20 amp Astron supply which are now on order from Astron. Then with the studs temporarily installed (no wires attached), I did a continuity check to ground and all was good, now the negative stud eventually does connect to ground and really does not matter but for poops and giggles I did it anyway.
I now connected the internal positive and negative wires to the studs and secured them. I then did the smoke test by turning on the power supply................all went well or this would be a much different blog post! I then tested the voltage at the Astron power supply new stud terminals and it was 13.86 VDC, then the cover when back on. I then added ring terminals to the Icom power cables (less the inline fuses and more on that in another post)
 |
| Marked and ready to go |
When I powered the Icom radio up and looked at the onboard voltage meter was reading 13.6 volts DC and during transmit using an FT8 carrier (into a dummy load) the voltage only dropped to 13.12 volts DC which is a great improvement.
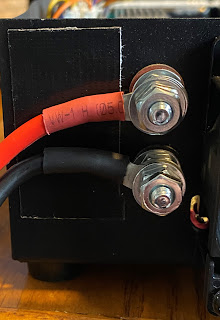 |
| Finish product |
Mike Weir, VE9KK, is a regular contributor to AmateurRadio.com and writes from New Brunswick, Canada. Contact him at [email protected].
 LHS Episode #504: OTA and Portable Ops Deep Dive
LHS Episode #504: OTA and Portable Ops Deep Dive
Hello and welcome to the 504th installment of Linux in the Ham Shack. In this episode, the hosts discuss the ins and outs of portable operations including *OTA stations. All topics are covered from hardware and software to space and weight considerations, power consumption, land use rights, expenses, operating procedures and much more. Thanks for listening and have a great week.
73 de The LHS Crew
Russ Woodman, K5TUX, co-hosts the Linux in the Ham Shack podcast which is available for download in both MP3 and OGG audio format. Contact him at [email protected].