Posts Tagged ‘shortwave’
 Livestream: Space WX, Propagation, Amateur Radio – Sundays
Livestream: Space WX, Propagation, Amateur Radio – Sundays
 Vacuum Tubes – Electronics at Work: 1943 Educational Film
Vacuum Tubes – Electronics at Work: 1943 Educational Film
In the classic educational film titled “Electronics at Work,” produced by Westinghouse in 1943, viewers are introduced to the fascinating world of vacuum tubes. This film highlights the crucial role these devices played in both military and commercial sectors, including radio telecommunications, radar, and various industrial applications. The narrative suggests that vacuum tubes provided the United States with a significant advantage during World War II, particularly in enhancing communication and technology.
The Continuing Relevance of Vacuum Tubes
Despite advances in technology, vacuum tubes remain in use today for several applications, including:
– Transmitting radios
– Medical devices
– Audio amplification systems
– High-frequency applications
Understanding Vacuum Tubes
The film outlines the six basic functions of electronic tubes and illustrates how each type is employed in different industrial and military contexts.
[embedyt] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZJ6rN7WEjbc[/embedyt]
Structure of a Vacuum Tube
A vacuum tube typically consists of two or more electrodes housed within a vacuum inside an airtight enclosure. Key features include:
– Electrode Types: Most vacuum tubes have glass envelopes, although some utilize ceramic or metal casings with insulating bases.
– Leads and Sockets: The electrodes connect to leads that pass through the envelope via an airtight seal. These leads often take the form of pins, allowing for easy replacement in a tube socket, as tubes were a common point of failure in electronic devices.
– Capacitive Design: Some tubes feature a top cap on the electrode to minimize interelectrode capacitance, enhancing high-frequency performance and maintaining safety by separating high voltages.
The Evolution of Vacuum Tubes
The earliest vacuum tubes emerged from incandescent light bulbs, which contained a heated filament sealed in an evacuated glass envelope. When heated, the filament releases electrons into the vacuum through a process known as thermionic emission.
– Electrode Functionality: A second electrode, known as the anode or plate, attracts these electrons if it holds a more positive voltage. This mechanism results in a flow of electrons from the filament (cathode) to the plate, creating an electric field due to the potential difference between them.
– Diode Function: A vacuum tube with two electrodes is termed a diode, which functions as a rectifier. Diodes allow current to flow in only one direction, converting alternating current (AC) into pulsating direct current (DC). This technology is widely used in DC power supplies and in demodulating amplitude-modulated (AM) radio signals.
Film Availability and Production Details
This film is available in the public domain under Creative Commons, and it can be accessed through the Library of Congress Prelinger Archives. The film has been edited and converted to HD quality for better viewing. Introductory and closing music is provided by Nero 10, with commercial use rights granted.
This film not only serves as an educational tool but also highlights the enduring legacy of vacuum tube technology in the realm of electronics, illustrating its significant contributions to both past and present technological advancements.
Please subscribe to my YouTube Channel: https://YouTube.com/NW7US
Also, please click on the bell, to enable alerts so that when I post a new video, you will be notified. By subscribing and making sure that the bell (alert) notification is set to ALL, you will be kept in the loop for new videos and more.
 German Teletype (RTTY) Weather on HF (Shortwave) Radio
German Teletype (RTTY) Weather on HF (Shortwave) Radio
This is a video of the German Weather Broadcast from DWD, Hamburg, on shortwave (HF), using teletype (RTTY). I demonstrate two decoding software options: JWcomm32 (older), and, FLdigi. Note the in FLdigi, the “Reverse” feather is selected to properly decode the signal (in either USB or LSB, you still need to select, “Reverse”).
The radio used to receive these weather bulletins is an Icom IC-7610, using an antenna designed for 160 Meters.
RTTY is a system for broadcasting text over radio. The technology dates back to the late 1950s and seems somewhat anachronistic. Speeds are slow, even slower than NAVTEX. A similar service is the USCG service, SITOR (Simplex Teletype Over Radio) providing offshore and coastal forecasts over very wide and remote areas from the tropics to the polar regions.
There is dedicated equipment to receive RTTY and SITOR but we can receive both using a standard HF/SSB receiver with software packages such as TRUETTY and SEATTY to decode the signals.
The main advantage of RTTY/SITOR is the reception of information over an entire ocean area. The USCG also shares frequencies across multiple transmitters according to a schedule, rather like NAVTEX. The system is available over the Atlantic and Pacific including polar regions not served. For more about SITOR see the Monitoring Times link or the USCG site.
Around Western Europe and the Mediterranean, the Deutscher Wetterdienst (DWD) , the German Weather Service has accepted the responsibility to broadcast weather information for mariners on RTTY. Frequencies are in the table on the webpage at:
https://weather.mailasail.com/Franks-Weather/Radio-Teletype-Weather-Broadcasts
This video captures the RTTY transmission on 14467.3 kHz (with adjustment in the passband to center on Mark and Space as seen in the video).
DWD (Hamburg) Broadcast Content:
Some broadcasts are of raw weather observations in a WMO coded form. Otherwise, for the broadcasts include,
- Strong wind, gale and storm warnings for German Bight, Western and Southern Baltic Sea, German North Sea and Baltic Sea coast
- Weather forecast for the North Sea and Baltic Sea, Weather situation, forecast valid for 12 hours and outlook valid for another 12 hours
- Weather report German North Sea and Baltic Sea coast, Weather situation and forecast valid for 12 hours.
- Navigational warnings for North Sea, Baltic Sea and German coast
- Weather report Norwegian Sea and Baltic Sea Route North Cape – Shetlands, The Quark – Gulf of Finland. Weather situation and time series forecast for 2 days
- Weather report North Atlantic. Route Pentlands – Southwest Greenland. Weather situation and time series forecast for 2 days
- Station reports North Sea and Baltic Sea
- Weather report Western European Sea. Route Southern Ireland – Area Canarias. Weather situation and time series forecast for 2 days
- Medium range weather report North Sea, Weather situation and time series forecast for 5 days
- For the Mediterranean there are Station reports Mediterranean Sea
- Weather report Mediterranean Sea (in German), Weather situation and forecast valid for 24 hours.
- Alborán – Tunis. Weather situation and time series forecast for 2 days
- Weather report Eastern Mediterranean Sea (in German). Route Eastern Tunis – Rhodes/Cyprus. Weather situation and time series forecast for 2 days
- Medium range weather report Mediterranean Sea (in English), Weather situation and time series forecast for 5 days
- Around the North Sea and the Baltic this service is a useful supplement to NAVTEX. Particularly so are the 5 day outlooks, These give wind forecast every 12 hours for the 5 day period. The values are straight from the DWD NWP model at a few grid points although these are sufficient to give an overall view and much quicker to receive than synoptic charts on radio fax.
In the Mediterranean, most valuable is the 5 day forecast which seems to be used and very highly regarded by the majority of serious cruising yachtsmen. It is a most valuable service for predicting the major strong wind systems such as Mistrals, Libeccios, Tramontanes, etc. Such winds are usually well predicted 4 and often 5 days ahead. Conversely, I have never found the 24 hour forecast to be much use. For this period, the French, Spanish and even the Italian NAVTEX broadcasts are to be preferred.
 1939 Film: Morse Code on HF in New Zealand (Historical)
1939 Film: Morse Code on HF in New Zealand (Historical)
Before modern radio broadcasting, the trails were being blazed both in public broadcast, but also critical links out of the local area. Here’s a side-look back in time…. in this 1939 Film: New Zealand Shortwave Communications; Morse code (CW)
The romance of the radiotelegraph service (in this video, the service in New Zealand) is a fascinating aspect of communication history. The use of shortwave, longwave, and medium frequency spectrum for communication, particularly through Morse code, played a significant role in connecting people across vast distances. This service utilized the high-frequency spectrum known as “shortwave” (from 3 MHz up to 30 MHz) as well as the longwave (30 kHz to 300 kHz) and medium frequency spectrum (300 kHz to 3 MHz).
This short film is from 1939, and captures the essence of communication at that time in history, to and from New Zealand using shortwaves and Morse code. It showcases the importance of the radiotelegraph service in enabling long-distance communication during that era. The transition from Morse code via spark-gap communications to continuous wave (CW) modulation marked a significant advancement in the technology and efficiency of radio communication.
It’s incredible to see how technology has evolved over the years, transforming the way we communicate and connect with each other globally. Films like these provide a glimpse into the past and remind us of the ingenuity and dedication of those who worked in the radiotelegraph service to ensure effective communication across the seas.
[embedyt] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=H-KUat5WEkU[/embedyt]
This film is a 1939 Government film scanned to 2K from a 16mm combined B/W reduction print.
 Marine Radiofax Weather Charts Via Shortwave Radio – WEFAX
Marine Radiofax Weather Charts Via Shortwave Radio – WEFAX
Weather out over oceans? That, and more.
More than international broadcast stations and amateur radio operators exist on the shortwave radio spectrum. For instance, any non-broadcast signal that is not amateur radio is often lumped together into a category known as Utility Radio, abbreviated, UTE. To dig deeper into UTE activity, you could check out the UDXF – the Utility DX Forum, located here: https://www.udxf.nl/
Utility stations (UTE) are quite common, from marine (ships, fishing vessels, etc.), transoceanic air traffic (international passenger or cargo jets and other aeronautical trans-oceanic radio traffic), to military radio (weather, coordination, and much more). UTE is a rich subdomain of the radio experience.
As an amateur radio operator, I listen to and monitor utility stations on shortwave, at times when not operating as an amateur radio station. I check weather for air traffic or for marine traffic, because it helps me see the larger-scale weather patterns.
Here is a video I made of my reception of weather charts via shortwave radio from radio station NMC, at Point Reyes, CA, using FLdigi software to receive these weather fax transmissions:
WEFAX 22.527 MHz on 2024 JUNE 14
[embedyt] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9N66y9HFX_Q[/embedyt]
This video is a screen and sound capture of my reception of weather charts and images by shortwave radio, from a station in California running about 4 kilowatts of RF power. This HF WEFAX (Weather Facsimile) service is on every day for ship (marine) weather dissemination so that ships out on the ocean can get weather charts and images not by satellite, but by receiving shortwave signals.
Below is a snippet from the published schedule from Point Reyes WEFAX Radio, callsign NMC, as follows:
22527 kHz – tune offset 1.9 kHz (see note, below)
UTC WHICH CHART ----- -------------------------------- 19:13 TROPICAL GOES IR SATELLITE IMAGE 19:23 WIND / WAVE ANALYSIS 19:33 96HR SURFACE FORECAST 19:43 96HR WIND/WAVE FORECAST 19:53 96HR 500MB FORECAST 20:03 96HR WAVE PERIOD / DIRECTION -------------------------------------
The above snippet of the NMC chart transmission list is from the page, “NMC Point Reyes, Marine Radiofax Broadcast Schedule” found at:
https://weatherfax.com/nmc-point-reyes/
Here is a detailed description of the weather charts, and online access is at:
https://www.weather.gov/marine/radiofax_charts
Note: In the video, you see that I am tuned to 22.526 USB thus I was tuned to 22526 kHz USB, based on this: “Unless otherwise stated, assigned frequencies are shown, for carrier frequency subtract 1.9 kHz. Typically dedicated radiofax receivers use assigned frequencies, while receivers or transceivers, connected to external recorders or PC’s, are operated in the upper sideband (USB) mode using carrier frequencies.”
==================================
Source:
WORLDWIDE MARINE RADIOFACSIMILE
BROADCAST SCHEDULES
U.S. DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE
NATIONAL OCEANIC and ATMOSPHERIC ADMINISTRATION
NATIONAL WEATHER SERVICE
April 12, 2024
https://www.weather.gov/media/marine/rfax.pdf
 Solar Cycle 25, and a Life-Changing Event (Part 1 of 2)
Solar Cycle 25, and a Life-Changing Event (Part 1 of 2)
From the RAIN HamCast episode #56, 2021-XII-11 (used with permission):
When you were knee high to a grasshopper, did you undergo a game-changing experience that shaped your future career?
Here is text from the introduction:
Tomas Hood/NW7US did. Tomas has been a shortwave enthusiast since 1973. He was first licensed as a ham in 1990 at age 25.
In the mid 1990s Tomas launched the first civilian space weather propagation website, HFRadio.org, which later spawned SunSpotWatch.com. His website, NW7US has been up and running since June, 1999. Tomas has contributed to the Space Weather Propagation column in CQ magazine for over 20 years, and for The Spectrum Monitor magazine since 2014.
A product of the Pacific northwest, Tomas resides today in Fayetteville, OH. RAIN’s Hap Holly/KC9RP spoke with Tomas recently about Solar Cycle 25 and the game-changing afternoon Tomas experienced in 1973 at age 8 ( Read more about this, at his amateur radio and space weather blog: https://blog.NW7US.us/ ).
Here is the first part of the two-part interview:
Mentioned in the interview is Skylab:
From Wikipedia’s article on Skylab: Skylab was the first United States space station, launched by NASA, occupied for about 24 weeks between May 1973 and February 1974. It was operated by three separate three-astronaut crews: Skylab 2, Skylab 3, and Skylab 4. Major operations included an orbital workshop, a solar observatory, Earth observation, and hundreds of experiments.

Tomas was drawn into space weather as a life-long passion, by inspiration from Skylab, and from the hourly propagation bulletin from the radio station WWV.
WATCH FOR THE NEXT EPISODE, PART TWO
This video is only part one. The RAIN HamCast will conclude Hap’s conversation with Tomas in RAIN HamCast #57, scheduled for posting Christmas Day.

Hap Holly, of the infamous RAIN Report (RAIN = Radio Amateur Information Network), is now producing The RAIN HamCast. The results are both on https://therainreport.com and on the RAIN HamCast YouTube channel, https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCUbNkaUvX_lt5IiDkS9aS4g
KEEP ON HAMMING!
The RAIN Hamcast is produced and edited by Hap Holly/KC9RP; this biweekly podcast is copyright 1985-2021 RAIN, All rights reserved. RAIN programming is formatted for Amateur Radio transmission and is made available under a Creative Commons license; downloading, sharing, posting and transmission of this ham radio program via Amateur Radio in its entirety are encouraged. Your support and feedback are welcome on https://therainreport.com. Thanks for YouTube Technical Assistance from Tom Shimizu/N9JDI.
 New Antenna: The Following Footprints Are of My CW Signals (2021-March-14 @ 04:00 to 04:20 UTC).
New Antenna: The Following Footprints Are of My CW Signals (2021-March-14 @ 04:00 to 04:20 UTC).
The following footprints are of my CW signals on 2021-March-14 at about 04:00 to 04:20 UTC.
Click on this image to see a larger version of this image:
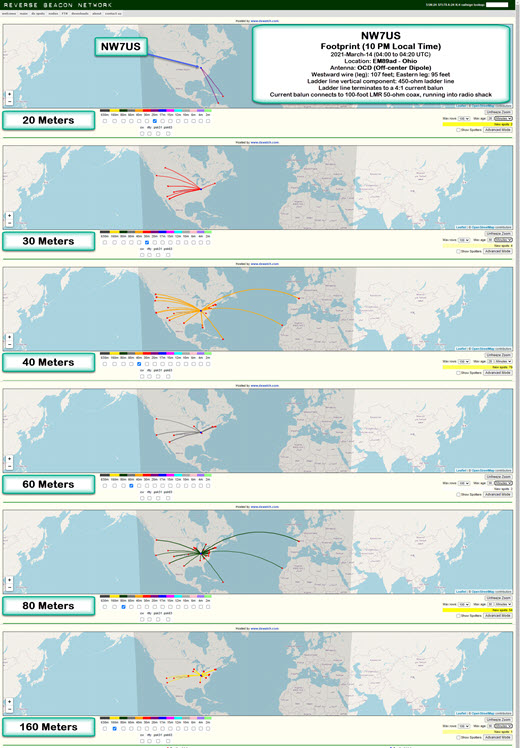
Location: EM89ad – Ohio
Antenna: OCD (Off-center Dipole)
Description of Antenna:
This is an off-center dipole, with the two legs running East-East-South (approximately 125 degrees of North), and West-West-North (about 306 degrees on the compass). The westward wire (leg) is approximately 107 feet in length, while the eastward leg is about 95 feet in length.
These legs (an off-center-fed dipole) is directly connected to about 90 feet of 450-ohm ladder line, which is hanging directly below, vertically, the feed point. The feed point is 50 feet above the ground.
The ladder line terminates (at the 12-feet-above-ground point) to a 4:1 current balun. This current balun then connects to a 100-foot LMR 50-ohm coax, which is running into the radio shack. It is connected via an antenna switch to my Icom IC-7610 transceiver. I am transmitting a 100-watt CW signal using an Icom IC-7610, in the following format:
TEST TEST TEST DE NW7US NW7US NW7US
The Reverse Beacon Network reports any spotting of this test transmission. The beta mapping interface, at http://beta.reversebeacon.net/main.php, then maps the resulting spots. To learn more about the RBN, visit http://beta.reversebeacon.net/index.php, or, http://reversebeacon.net/index.php.
I show the 20-, 30-, 40-, 60-, 80-, and 160-Meter band footprints.
I’ve been capturing these CW transmission spots, at different times of the day, today. I’ll get data from several days, at regular intervals, and create a overview of how the antenna appears to be working during this month and under these propagation conditions.
73 de NW7US dit dit
..















